Artificial Intelligence (AI) has fundamentally transformed numerous industries, and the recruitment sector is no exception. From improving efficiency to enabling scalability, AI has become an indispensable tool for HR teams across the globe. However, the introduction of agentic AI has taken things a step further. Unlike traditional AI, which often relies on human oversight, agentic AI operates autonomously, proactively analyzing data, learning from it, and executing tasks with minimal human intervention. This groundbreaking shift promises to redefine how organizations approach talent acquisition, offering a more intelligent, efficient, and dynamic recruitment process.
Why Legacy Hiring Systems Are Falling Behind?
Despite the advancements in AI and automation, many recruitment infrastructures remain rooted in legacy systems. These systems, often designed for in-office and linear workflows, have not evolved as quickly as the demands of the modern workforce. While many recruitment platforms have digitized paper-based processes, such as posting job advertisements, tracking applicants, and sorting resumes, they have not necessarily re-engineered them.
In essence, traditional recruitment systems still lean heavily on human decision-making. While the automation of tasks such as resume screening and interview scheduling has alleviated some of the manual burden, significant challenges remain, particularly around remote hiring, real-time management, and advanced talent analytics. Even with the integration of “smart” hiring tools like chatbots and automated screening, these platforms still rely on human oversight to make final decisions. This dependence can create bottlenecks in the hiring process, making it difficult for organizations to scale and adapt quickly to the evolving talent market.
The Three Waves of Hiring Tech
The recruitment landscape has undergone a significant transformation, moving through three major stages: basic automation, enhanced intelligence, and autonomous agency. Here’s how each stage has influenced the evolution of recruitment.
Basic Automation
The first stage of automation focuses on automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks. These include reviewing resumes, scheduling interviews, sending follow-up emails, and other administrative tasks. While these improvements have made hiring more efficient, they have often resulted in limited insight, as human judgment is still required to make decisions based on the data.
Enhanced Intelligence
In the second stage, recruitment systems became more intelligent. Rather than just automating tasks, these systems began to support decision-making by providing insights and recommendations. AI-powered tools could analyze data to suggest potential candidates for a role, but human involvement was still necessary to make final hiring decisions. While these systems enhanced the speed and accuracy of recruitment, they were still limited by their reliance on human judgment and oversight.
Autonomous Agency
The third and final stage in the evolution of recruitment technology is autonomous agency. This phase is characterized by the emergence of agentic AI systems. Unlike earlier AI tools, agentic AI is capable of operating autonomously, analyzing large volumes of data, learning from it, and making decisions in real-time with minimal human intervention. These systems can proactively engage candidates, adjust search parameters as hiring needs evolve, and continuously improve their performance based on feedback and data analysis. Agentic AI takes the concept of automation to a whole new level, providing organizations with a truly intelligent, self-improving hiring solution.
The Agentic Hiring Model
An agentic hiring system is built on a modular architecture, where specialized agents work together autonomously to optimize the recruitment process. Each agent is designed to perform a specific function, contributing to a seamless, integrated hiring experience.
- Sourcing Agents: These agents are responsible for identifying and enriching candidate profiles. By leveraging data from social media, professional networks, and talent databases, sourcing agents proactively identify top talent and expand the candidate pool.
- Vetting Agents: Vetting agents conduct candidate interviews, evaluating technical skills, behavioral traits, and cultural fit. These agents use sophisticated algorithms to assess not only qualifications but also how well a candidate will integrate into the organization’s culture.
- Matching Agents: These agents match candidates to open roles by analyzing behavioral, technical, and experiential data. The matching process goes beyond simply checking qualifications, considering factors like career progression, values alignment, and team dynamics.
- Feedback Agents: Once a hiring decision is made, feedback agents analyze the outcomes of the process. They identify patterns, evaluate the effectiveness of previous decisions, and refine the models that guide future hiring decisions, ensuring continuous improvement.
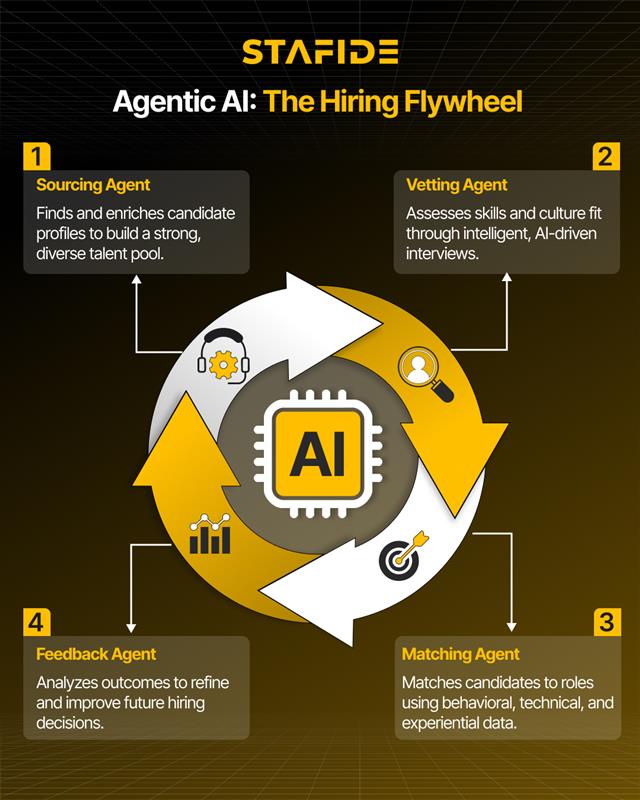
The seamless collaboration between these agents ensures that the hiring process is efficient, scalable, and continuously optimized.
Foundations of Smart Hiring Infrastructure
Building an intelligent hiring infrastructure that leverages agentic AI requires a careful and thoughtful approach. To create a successful, scalable, and reliable recruitment system, several key principles should be adhered to.
1. Collaborative Modular Architecture
The use of a modular architecture allows different agents to specialize in specific tasks while collaborating toward a common goal. This approach ensures that each agent can operate independently without compromising the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the hiring system.
2. Transparency and Trust
Trust is critical to the successful adoption of AI in recruitment. For organizations to fully embrace agentic AI, it is essential that the decision-making process is transparent and interpretable. Candidates, hiring managers, and other stakeholders should be able to understand why certain decisions were made, ensuring accountability and fostering trust in the system.
3. Global and Industry Adaptability
To meet the demands of a global workforce, intelligent hiring systems must be versatile enough to adapt to various geographies, languages, and industry-specific needs. This adaptability allows organizations to scale their recruitment efforts and hire talent from diverse backgrounds without losing the nuances that different regions and sectors require.
4. Prioritizing the Candidate Experience
At the core of any intelligent hiring system should be a candidate-first approach. This means creating a process that is transparent, respectful, and fair. From the initial application to the final offer, candidates should feel that they are treated with dignity, fairness, and clear communication.
Human Oversight and Ethical Considerations
As AI systems take on more decision-making in recruitment, the role of humans must evolve. Historically, hiring managers have been deeply involved in the recruitment process, but with the rise of intelligent hiring systems, their role is shifting toward strategic oversight and governance. While AI systems can handle most of the decision-making, humans will still be needed to ensure that the systems are aligned with the organization’s values and objectives.
This shift raises important ethical considerations. AI-powered hiring systems must be designed to mitigate bias, ensure fairness, and protect candidate data. Transparency, explainability, and accountability will be key to maintaining trust in these systems, especially as they make increasingly autonomous decisions.
The long-term societal impact of AI in recruitment also cannot be ignored. It is essential that these systems are designed to promote equity, not just efficiency. As AI systems become more integrated into the hiring process, business leaders must carefully consider the implications of their use and the potential consequences of biases or misalignments with the organization’s values.
Risks and Realities of AI-Driven Recruitment
While the potential of agentic AI is enormous, there are several risks and challenges that business leaders should keep in mind.
1. Lack of Governance
One of the primary concerns with agentic AI is the assumption that these systems can operate entirely autonomously. While AI can scale decision-making, errors can also scale quickly. Without appropriate guardrails and oversight, agentic AI systems could perpetuate biases, misinterpret candidate intent, or over-optimize for short-term goals, such as hiring speed, at the cost of long-term fit.
2. Transparency Issues
Another challenge with agentic AI is transparency. Many AI systems, particularly those based on deep learning, are often considered “black boxes,” meaning that the decision-making process is not easily understood. This lack of transparency can hinder trust, both internally and externally, and may lead to compliance challenges, especially in regions with strict data protection regulations.
3. Shifting Organizational Culture
Adopting agentic AI in recruitment is not just a technological shift it is a cultural one. It requires organizations to rethink how they approach hiring, how decisions are made, and how accountability is structured. For companies that are still operating with legacy systems and processes, this transformation can be challenging. Rushing the adoption of agentic AI can lead to confusion and inefficiencies, rather than a seamless transition.
The Road Ahead for AI in Recruitment
The future of recruitment will undoubtedly rely on intelligent systems that can handle tasks such as sourcing, interviewing, and onboarding. AI-powered virtual recruiters could become the default interface between hiring teams and candidates. Moreover, organizations will likely move away from siloed hiring processes toward more integrated global talent networks.
However, as companies embrace agentic AI, they must also remain mindful of the challenges and risks involved. A well-thought-out approach to implementation, along with careful governance and strategic oversight, will be essential to realizing the full potential of intelligent hiring systems. Ultimately, recruitment is one of a company’s most strategic investments, and the systems organizations build today will determine the speed, scale, and fairness of their workforce tomorrow.
In conclusion, agentic AI has the potential to revolutionize recruitment, but it must be adopted thoughtfully and responsibly. With the right approach, businesses can harness the power of AI to build more efficient, effective, and equitable hiring processes.
Redefining Talent Acquisition with Stafide
At Stafide, we don’t just follow trends we build the future. As a next-generation recruitment partner, we help organizations harness cutting-edge AI and agentic hiring models to identify, engage, and onboard the right talent at scale while ensuring every step is grounded in fairness, transparency, and human oversight for ethical, unbiased outcomes.
Let’s shape the future of hiring together.
Contact Stafide today to elevate your talent strategy.





